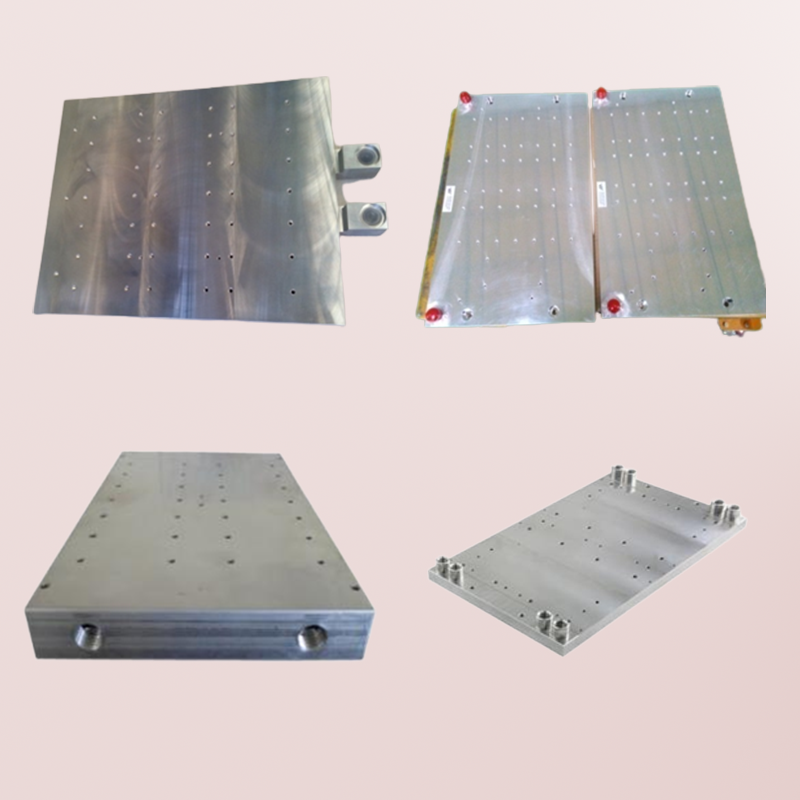
Cold Plates
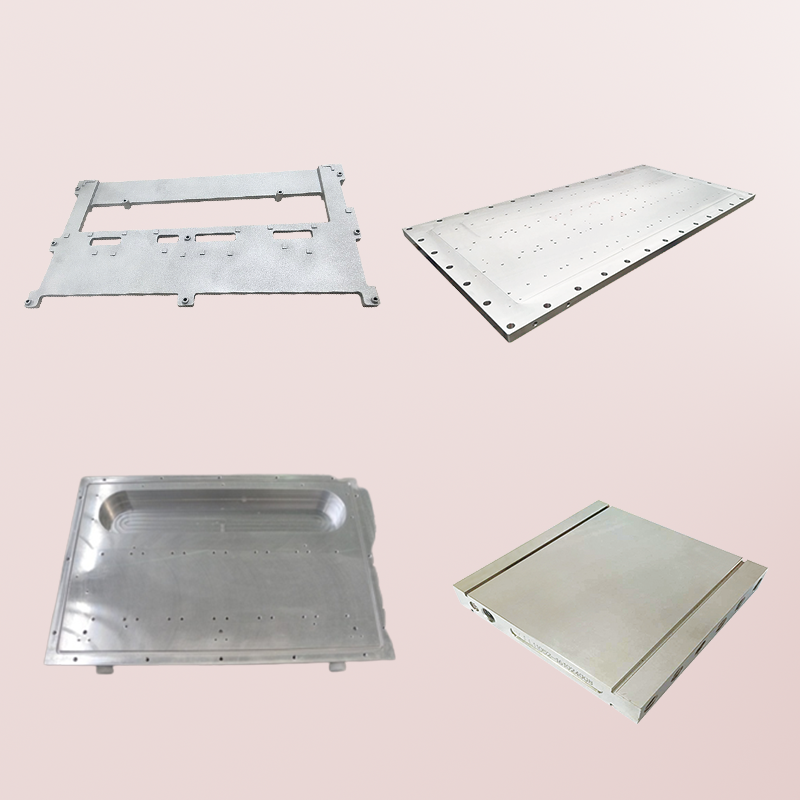
A cold plate, also known as a heat sink plate or liquid cooling plate, is a device used for thermal management in various applications, particularly in electronic and power systems. It is designed to efficiently transfer heat away from heat-generating components and dissipate it into the surrounding environment.
Description
A cold plate, also known as a heat sink plate or liquid cooling plate, is a device used for thermal management in various applications, particularly in electronic and power systems. It is designed to efficiently transfer heat away from heat-generating components and dissipate it into the surrounding environment.
Here are some key features and applications of cold plates:
- Design and Construction: Cold plates are typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum. They have a flat, planar surface with internal channels or fins for the flow of coolant or refrigerant.
- Heat Transfer: The primary function of a cold plate is to remove heat from heat sources, such as power electronics, processors, or high-power components. The cold plate makes direct contact with the heat source, allowing efficient heat transfer through conduction.
- Cooling Methods: Cold plates can employ different cooling methods, including liquid cooling and phase change cooling. In liquid cooling, a coolant, such as water or a specialized cooling fluid, circulates through the internal channels of the cold plate, absorbing heat and carrying it away. Phase change cooling involves the use of a refrigerant that changes phase from liquid to gas, absorbing heat in the process.
- Customization: Cold plates can be customized to fit specific applications and thermal requirements. They can be designed with specific channel geometries, sizes, and mounting options to provide optimal heat dissipation for the targeted heat source.
- Power Electronics and IT Equipment: Cold plates are commonly used in power electronics applications, including power converters, inverters, motor drives, and high-power semiconductor devices. They help manage the heat generated by these components, ensuring their optimal performance and reliability. Cold plates are also utilized in IT equipment, such as servers, data centers, a nd high-performance computing systems, to control heat generated by processors and other heat-intensive components.
- Energy and Aerospace Systems: Cold plates find applications in energy systems, including wind turbines, solar inverters, and energy storage systems, where efficient heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining system performance. They are also employed in aerospace and aviation applications, such as avionics cooling and thermal management in aircraft, to ensure reliable operation under extreme conditions.
- Medical and Laser Systems: Cold plates are used in medical equipment, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, laser systems, and ultrasound devices, to manage heat generated by electronic components and maintain stable operating temperatures.
Cold plates provide an effective means of thermal management, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating of sensitive electronic and power components. By efficiently dissipating heat, cold plates contribute to the reliability, performance, and longevity of various systems in diverse industries.







Leave a Comment